Features • Quick Start • Documentation • Validation • Contributing
EnSim is an open-source desktop application for rocket propulsion analysis and flight simulation. It combines NASA-validated thermochemical equilibrium calculations with full 6-DOF trajectory simulation, all within a modern, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're a student learning rocket science, a researcher exploring propulsion concepts, or an engineer performing preliminary design analysis, EnSim provides the tools you need.
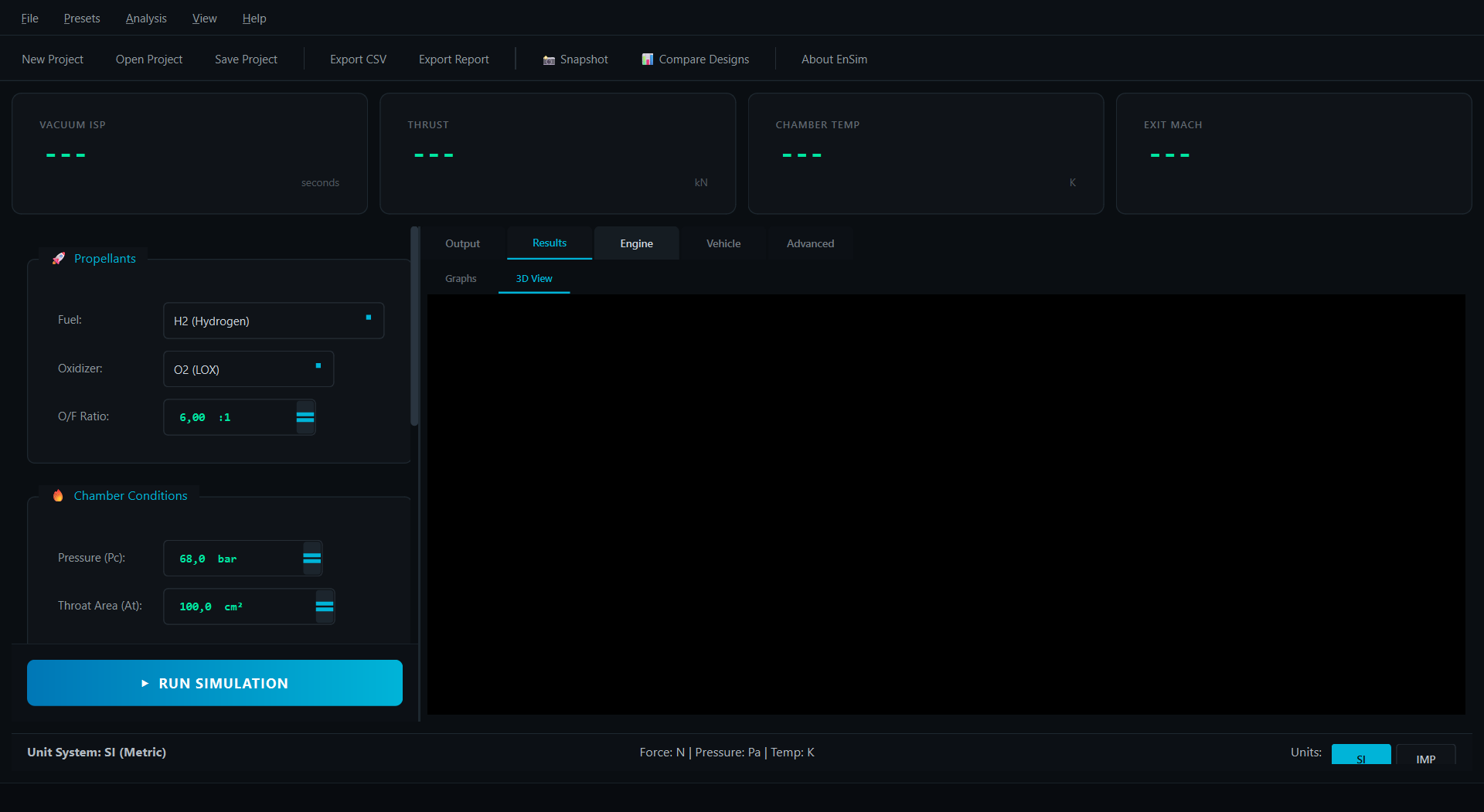
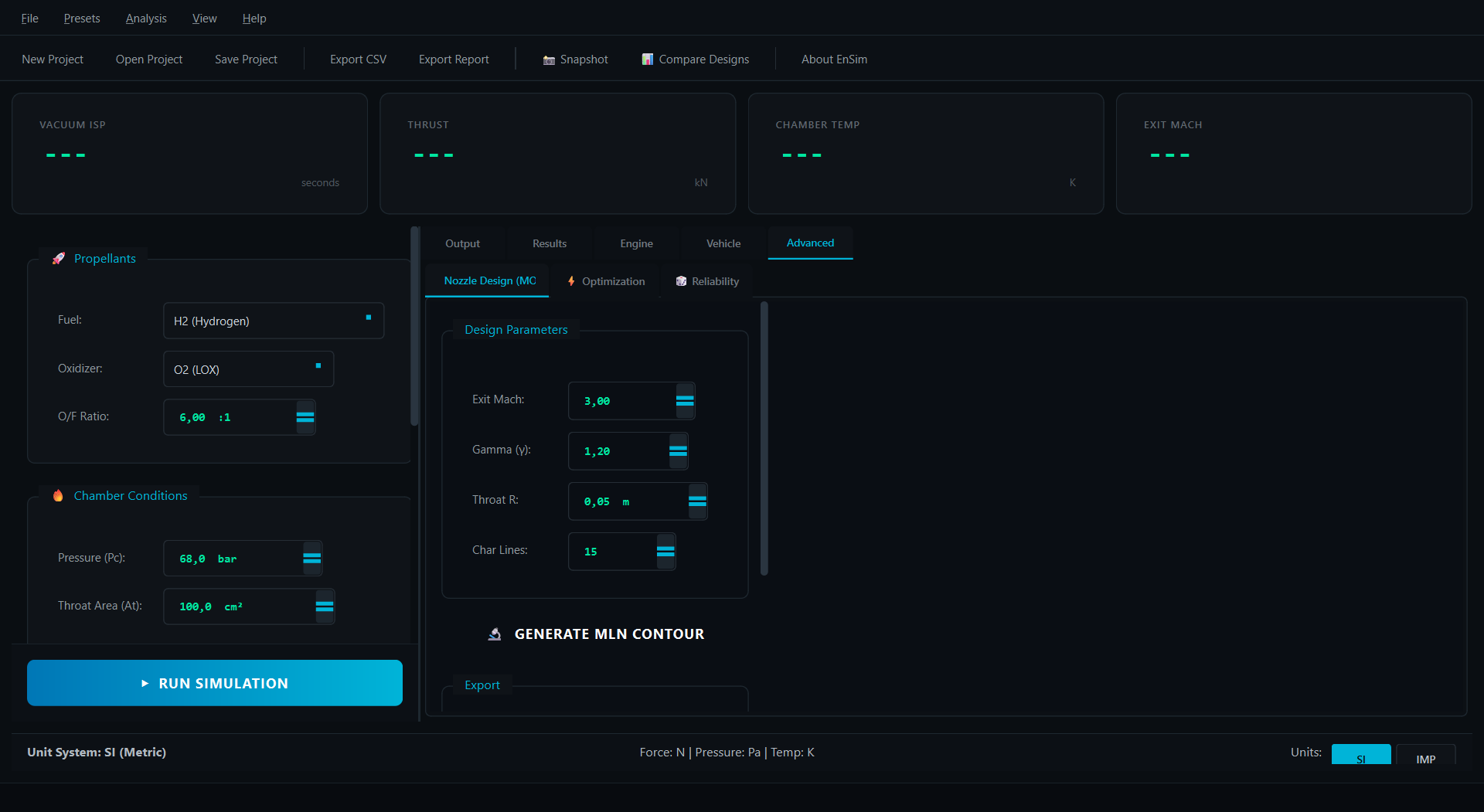
Click to expand screenshots
- NASA CEA Methodology: Gordon-McBride equilibrium solver with Gibbs free energy minimization
- Comprehensive Species Database: 35+ species including H₂, O₂, CH₄, RP-1, N₂O₄, UDMH, MMH
- High-Temperature Dissociation: Full accounting for H, O, OH, NO, and other radicals
- Validated Accuracy: <2% error vs NASA CEA reference data
- Chamber Temperature: Adiabatic flame temperature with dissociation
- Characteristic Velocity (C)*: Key measure of combustion efficiency
- Specific Impulse (Isp): Both vacuum and sea-level values
- Thrust Coefficient (Cf): With nozzle divergence corrections
- Full Rigid Body Dynamics: Quaternion-based orientation (no gimbal lock)
- Adaptive Integration: RK45 Dormand-Prince with automatic step sizing
- Aerodynamic Models: Configurable drag and stability derivatives
- Dense Output: Cubic Hermite interpolation for smooth trajectories
- Landing Dispersion: CEP and 3-sigma confidence ellipses
- Performance Variability: Statistical analysis of Isp, thrust, burn time
- Parallel Processing: Multi-core execution for thousands of runs
- Visualization: Scatter plots, histograms, and probability contours
- Multi-Stage Vehicles: Full staging simulation with preset rockets (Falcon 9, Saturn V)
- Regenerative Cooling: Bartz correlation thermal analysis with channel design
- Trajectory Optimization: Nozzle expansion ratio and stage mass allocation
- Materials Database: 10 aerospace materials with thermal properties
- 17 Propellant Presets: Ready-to-use fuel/oxidizer combinations
- Mission Control Aesthetic: SpaceX-inspired dark theme with cyan/green neon accents
- Real-time KPI Dashboard: Live display of key performance metrics
- Interactive 3D Visualization: PyVista-powered nozzle and trajectory display
- SI/Imperial Units: One-click unit system toggle
- Professional Exports: CSV data, Markdown reports, STL/OBJ/PLY 3D models
- Python 3.10 or higher
- pip package manager
pip install ensim# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/SpaceEngineerSS/EnSim.git
cd EnSim
# Create virtual environment (recommended)
python -m venv venv
# Activate virtual environment
# Windows:
venv\Scripts\activate
# Linux/macOS:
source venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt# Launch the GUI application
python main.py
# Run with validation tests
python main.py --test- Select Propellants: Choose fuel (e.g., H₂) and oxidizer (e.g., O₂)
- Set Conditions: Enter O/F ratio, chamber pressure, expansion ratio
- Run Simulation: Click "RUN SIMULATION" to calculate performance
- Analyze Results: View KPIs, graphs, and 3D nozzle visualization
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| ARCHITECTURE.md | System design and physics overview |
| docs/THEORY.md | Mathematical formulation and equations |
| docs/VALIDATION.md | NASA CEA comparison results |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Contribution guidelines |
| CHANGELOG.md | Version history |
EnSim is rigorously validated against NASA CEA, the industry standard for rocket propulsion analysis.
| Propellant Combination | T_chamber Error | Isp Error | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOX/LH₂ | 1.76% | 1.41% | ✅ Pass |
| LOX/CH₄ | 0.48% | 1.07% | ✅ Pass |
| LOX/RP-1 | 0.49% | 0.86% | ✅ Pass |
| N₂O₄/UDMH | 0.56% | 0.85% | ✅ Pass |
Overall Accuracy: Average error <1% across all validated cases
See VALIDATION.md for detailed comparison data.
EnSim/
├── 📁 src/
│ ├── 📁 core/ # Physics Engine (Numba JIT)
│ │ ├── chemistry.py # Gibbs equilibrium solver
│ │ ├── propulsion.py # Nozzle flow calculations
│ │ ├── flight_6dof.py # 6-DOF dynamics
│ │ ├── integrators.py # RK45, Hermite interpolation
│ │ ├── monte_carlo.py # Dispersion analysis
│ │ └── thermodynamics.py # NASA polynomial evaluation
│ │
│ ├── 📁 ui/ # User Interface (PyQt6)
│ │ ├── windows/ # Main window, dialogs
│ │ ├── widgets/ # Custom widgets
│ │ └── workers.py # Background threads
│ │
│ └── 📁 utils/ # Utilities
│ ├── nasa_parser.py # Thermo data parser
│ └── exporters.py # Data export functions
│
├── 📁 data/ # NASA thermodynamic database
├── 📁 tests/ # Test suite (pytest)
├── 📁 docs/ # Documentation
└── 📁 assets/ # Icons, stylesheets
| Component | Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| GUI | PyQt6 | Modern cross-platform interface |
| Numerics | NumPy, SciPy | Array operations, optimization |
| Acceleration | Numba | JIT compilation for 10-100x speedup |
| 3D Visualization | PyVista | Interactive nozzle/trajectory display |
| 2D Plots | Matplotlib | Scientific plotting |
| Testing | pytest | Unit and validation tests |
We welcome contributions from the community! Whether it's:
- 🐛 Bug Reports: Found an issue? Open a bug report
- ✨ Feature Requests: Have an idea? Suggest a feature
- 🔬 Scientific Issues: Validation concerns? Report a scientific issue
- 💻 Code Contributions: Ready to code? See CONTRIBUTING.md
# Install development dependencies
pip install -e ".[dev]"
# Run tests
pytest tests/ -v
# Run linting
ruff check src/
# Format code
black src/ tests/This project is licensed under the MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
- NASA Glenn Research Center - Thermodynamic polynomial database
- Sutton & Biblarz - "Rocket Propulsion Elements" reference
- The open-source scientific Python community - NumPy, SciPy, Matplotlib
-
Gordon, S. & McBride, B.J. (1994). "Computer Program for Calculation of Complex Chemical Equilibrium Compositions and Applications". NASA Reference Publication 1311.
-
McBride, B.J., Zehe, M.J., & Gordon, S. (2002). "NASA Glenn Coefficients for Calculating Thermodynamic Properties of Individual Species". NASA/TP-2002-211556.
-
Sutton, G.P. & Biblarz, O. (2017). "Rocket Propulsion Elements". 9th Edition, Wiley.
-
Anderson, J.D. (2003). "Modern Compressible Flow". 3rd Edition, McGraw-Hill.
Made with ❤️ for the aerospace community